January 05, 2012
 Locked out of your house in the middle of the night? Have you lost the key to the padlock on the shed? Before you pay a locksmith to let you in or to open something up, consider picking the lock yourself. Most locks around the home or office are simple pin-and-tumbler locks and can be relatively easy to open using a pick and tension wrench, both of which can be improvised from common household items. While the process is simple and can be mastered with practice, picking such a lock requires a great deal of patience. To pick locks, a person has to insert a thin metal pin or needle, moving the pin around until hearing a click or a gear shift. This article will show you how to pick a lock.
Locked out of your house in the middle of the night? Have you lost the key to the padlock on the shed? Before you pay a locksmith to let you in or to open something up, consider picking the lock yourself. Most locks around the home or office are simple pin-and-tumbler locks and can be relatively easy to open using a pick and tension wrench, both of which can be improvised from common household items. While the process is simple and can be mastered with practice, picking such a lock requires a great deal of patience. To pick locks, a person has to insert a thin metal pin or needle, moving the pin around until hearing a click or a gear shift. This article will show you how to pick a lock.
Steps
- Understand how your lock works. The pin-and-tumbler lock consists of a cylinder that can rotate within its housing (see illustrations below). When locked, the cylinder is kept in place by several pairs of pins. The top pin of each pair protrudes into both the cylinder and the housing, thus preventing the cylinder from turning. When the correct key is inserted, it pushes the pairs of pins up so that the top pins no longer enter the cylinder. When this happens, the cylinder can be turned and the lock will open.
- Note the five pairs of pins. The blue pins enter both the cylinder and the (green) housing around it, thus preventing the cylinder from turning. The springs provide resistance to keep the pins in place.
Hilton Shopping Gallery
Housing luxury brands & Fashion Located in Orchard Road, Singapore www.hiltonshoppinggallery.com |
| Note the five pairs of pins. |
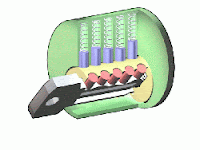
- Get a pick and tension wrench. Each pick is specialized for a different problem. A tension wrench, or torque wrench, is the device which you apply pressure with to turn the lock cylinder. Professional-grade picks and tension wrenches can be purchased in sets (see picture), but many lock picking hobbyists make good quality sets of their own. See the Things You'll Need section below for information on how to make your own picks and tension wrenches.

- Place the tension wrench into the lower portion of the keyhole.
- Determine which way the cylinder must be turned to unlock the lock. If you commonly use the lock, you probably already know which way you turn the key to open the lock. If you don’t know, use the tension wrench to apply torque to the cylinder, first clockwise and then counterclockwise. The cylinder will only turn a fraction of an inch before it stops. Try to feel the firmness of the stop. If you turn the cylinder the wrong way, the stop should feel very firm and stiff. If you turn it the right way, there should be a bit more give. Some locks, especially among padlocks, will open regardless of which way the cylinder is turned.
- Apply light torque to the tension wrench in the correct direction, and hold. The required torque will vary from lock to lock and from pin to pin, so this may require some trial and error. Start gently, though.
- Insert the pick into the upper part of the keyhole and feel the pins. With the pick in the keyhole, you should be able to press up and feel the individual pins with the tip of the pick. You should be able to push them up and feel them spring back down when you release the pressure. Try to push each one all the way up. Identify which one is the hardest to push up. If they are all very easy to push up, turn your tension wrench more to increase the torque. If one won’t go up at all, ease the torque until you can push it up. Alternately, you may wish to “rake” the pins before this step (see Tips below).

- Push the stubborn pin up until it “sets.” Press the stubborn pin with just enough pressure to overcome the downward pressure of the spring. Remember, the pin is actually a pair of pins. Your pick is pushing against the lower pin, which in turn pushes against the upper pin. Your goal is to push the upper pin completely out of the cylinder. Then, when you stop pushing, the lower pin will fall back down into the cylinder, but the torque on the cylinder will result in a misalignment of the hole in the cylinder with the hole in the housing, and the upper pin should then rest on the cylinder without falling back down. You should hear a faint click as the upper pin falls back down on top of the cylinder. You should also be able to push the lower pin up a little with no resistance from the spring when this occurs you most likely have the upper pin “set.”
- Continue applying torque and repeat the last two steps for each of the remaining pins. It is imperative that you maintain torque on the cylinder to prevent the set pins from dropping back down. You may need to make slight increases or decreases in torque for each pin.
- Use the tension wrench to turn the cylinder and unlock the lock. Once all the pins are set, you should be able to turn the cylinder. Hopefully you have already ascertained the correct direction to turn it. If you have chosen the wrong direction, you will need to start over and reset all the pins.
Hilton Shopping Gallery
Housing luxury brands & Fashion Located in Orchard Road, Singapore
www.hiltonshoppinggallery.comCutlass Stud Welding
Detailed technical information on studs and stud welding systems
www.cutlass-studwelding.comRelocating to/from Kuwait
Looking for a professional moving company for your move, please visit
www.moving.gac.com











0 komentar:
Posting Komentar